As I’ve previously written, South-South migration — migration within and between poor countries — deserves attention in our understanding of global migration, and we can be inspired by scholars of migration and development who have worked hard on this. India is an important example: it is a large, fast-growing, but quite poor country (in per capita terms) surrounded by neighbors who are somewhat poorer in per capita terms and much smaller in size. I previously wrote part 1 of a two-part series on open borders within India and also looked at the existence of open borders between India and Nepal.
The topic of this post is more difficult: policy options for migration between Bangladesh and India. The lack of easily available public material on the subject, combined with my relative ignorance, make me an inappropriate candidate to delve into the relevant empirics and historical details. I’ve asked some others to do guest posts for the site on the subject, and these will hopefully materialize later this year. But, given that I consider the case for open borders to be universal, I should be able to provide an approximate contour of how I believe the case applies to India and Bangladesh. That’s what I try to do here.

Population and income differences
India’s population is about 1.21 billion and per capita GDP (PPP) estimates range from $4000 to $6000. Bangladesh has a population of about 157 million and per capita GDP (PPP) estimates range from $2100 to $3300. The estimates co-vary, i.e., the sources that estimate higher GDP (PPP) per capita for India estimate proportionately higher GDP (PPP) per capita for Bangladesh. You can see a few lists at this page.
Essentially, Bangladesh has about 13% the population and 60% the per capita GDP that India does.
The population ratio seems huge but not terribly so: even if all Bangladeshis migrated to India over a period of a decade, the effect on the Indian population as a whole would not be huge. On the other hand, current patterns of Bangladeshi migration, whereby they settle primarily in border states, may not be scalable to very large migration levels. I believe it is likely that, if borders were more formally opened, migrants from Bangladesh would move out farther to other parts of India, rather than primarily landing up in the nearby states of West Bengal and Assam. Also, I don’t think Bangladesh would empty out. Rather, the situation would probably be similar to that of Nepal and India: no immediate large-scale exodus, but over a longer timeframe, the “Bangladeshi diaspora” in India would grow to a size comparable with the population that is left in Bangladesh. Note that GDP (PPP) per capita in Nepal is lower than in Bangladesh, so if anything, pure economic pressure to migrate should be lower from Bangladesh. But there are some other differences, that we turn to next.

The GDP per capita differences with the bordering states are not so severe. According to a list of gross state domestic products for Indian states, West Bengal is close to the national average and does reasonably better than Bangladesh. Assam does only slightly better than Bangladesh, and the other North-Eastern states do about the same or worse. Ironically, part of the reason for the relative underdevelopment of these states is their relatively poor land connectivity with the rest of India, and that poor land connectivity is because of the geographical location of Bangladesh. As I mention later in the post, allowing freedom of movement through Bangladesh can facilitate greater economic integration of these states.
Why do Bangladeshis migrate to nearby states despite small income differences? I suspect there are many reasons, including long-term cultural connections, but there is also the advantage of being part of an economy that is on the whole larger, faster-growing, and more promising. Once they are in India, they can more easily move to other parts of India — even if most of them don’t avail of the opportunity. Another factor could be weather-related problems leading people to migrate temporarily or permanently out of where they live in Bangladesh.
Differences with Nepal
I’ll repeat some differences I listed in my post on open borders between India and Nepal:
- Population: Bangladesh has a population of 150 million, about 5-6X the population of Nepal. So, having open borders with Bangladesh is (considered) less feasible, or at any rate, would be a bigger and more transformative change.
- Greater cultural similarity propelling more migration: Bangladeshis share close cultural roots with West Bengal (indeed, Bangladesh and West Bengal were both part of the state of Bengal in British India). Thus, there is likely to be much greater migration of Bangladeshis since they may have more confidence they’ll be able to adjust to life in West Bengal. (In practice, due to reasons of geography and the strength of border security, many Bangladeshis migrate to Assam rather than West Bengal).
- Religion: Bangladesh is an officially Muslim country with a Muslim majority. Although not as hostile to India as Pakistan, it still has some hostility. Nepal is a Hindu majority country with small amounts of Buddhism and Islam — religious demographics very similar to India.
- Historical accident: Bangladesh and India actually started off somewhat well, because India supported Bangladesh (then East Pakistan) in its struggle for independence against West Pakistan (~1971). But political changes in Bangladesh led to a worsening of relations.
Bangladeshi migration: raw numbers
As with most historical South-South migration, the current situation can be very open in practice for migrants. Or at least it has been until recent changes. An estimate of somewhere between 3 million and 20 million illegal immigrants from Bangladesh to India is a similar magnitude to the number of illegal immigrants from Mexico to the United States (about 7 million) and even comparable to the total illegal immigrant population of the United States (about 11-13 million being the median estimate, though there is again uncertainty). The number is smaller as a proportion of the population of India, which is more than 3.5 times the US population. This might explain the lower national salience in India of Bangladeshi immigration. On the other hand, the geographical concentration of Bangladeshi immigrants in West Bengal and Assam means greater regional salience of the issue.
Cultural camouflage
Here’s what Wikipedia says:
As per 2001 census there are 3,084,826 people in India who came from Bangladesh[1] No reliable numbers on illegal immigrants are currently available. Extrapolating the census data for the state of Assam alone gives a figure of 2 million.[3][4] Figures as high as 20 million are also reported in the government and media.[5][6] Samir Guha Roy of the Indian Statistical Institute called these estimates “motivatedly exaggerated”. After examining the population growth and demographic statistics, Roy instead states that a significant numbers of internal migration is sometimes falsely thought to be immigrants. An analysis of the numbers by Roy revealed that on average around 91000 Bangladeshis nationals might have crossed over to India every year during the years 1981-1991 but how many of them were identified and pushed back is not known. It is possible that a large portion of these immigrants returned on their own to their place of origin.[7]
According to one commentator, the trip to India from Bangladesh is one of the cheapest in the world, with a trip costing around Rs.2000 (around $30 US), which includes the fee for the “Tour Operator”. As Bangladeshi are cultural similar to the Bengali people in India, they are able to pass off as Indian citizens and settle down in any part of India to establish a future.,[8] for a very small price. This false identity can be bolstered with false documentation available for as little as Rs.200 ($3 US) can even make them part of the vote bank.
The cultural camouflage that Bangladeshi migrants can engage in reflects two truths: first, the absence of an all-knowing state that has documentation and records for all existing citizens (this might be changing, though, with new identification and documentation schemes being implemented). Second, the genuine historical and cultural connection between West Bengal and Bangladesh, that were one Indian state under British Rule prior to the Partition of India in 1947 (in fact, an attempted partition back in 1905 by the British had to ultimately be reversed after significant opposition). To the extent that there are no obvious differences between Indian Bengalis and Bangladeshis, it would seem that this should point in the direction of officially recognizing the freedom of movement, since it seems to obviate concerns regarding assimilation. But political commentators, who are keen to enforce the sanctity of borders and the formal concept of citizenship, often bemoan rather than celebrate the difficulty of distinguishing Bangladeshis from genuine Indian Bengalis:
Commonality of language, culture and religion between the two countries emerged as a major challenge in identifying immigrants, making deportation extremely difficult. The immigrants speak the same language as many Indians, and often have familial connections that make it easy to assimilate with the local population. Bangladesh’s consistent denial that its citizens are illegally crossing the border also complicates matters. Even when Indian authorities have identified illegal immigrants, deporting them becomes almost impossible given the reluctance of Bangladeshi authorities to cooperate.
An underdeveloped deportation machinery
As I wrote in my South-South migration post:
In some ways, the current nature of South-South migration as well as the social and political attitudes to it closely resemble 18th and 19th century migration worldwide. People moved from very poor countries to less poor countries with more vibrant cities and growth opportunities. Natives weren’t exactly thrilled, but strong anti-migration sentiment, while often virulent by modern standards, was relatively localized and took a fair amount of time to translate to successful national movements to curb migration. I’m not aware of survey data similar to the World Values Survey for the 19th century, but my guess is we’d see a similar 25-25-25-25 split about migration despite more overtly prejudicial attitudes among the people (similar to the situation in India today).
This connects with my very first post on the Open Borders site, where I blegged readers on why immigration was freer to the 19th century USA. I had listed three potential reasons in that post: (1) wisdom/desirability, (2) technological/financial feasibility, and (3) moral permissibility. At the time, I had written that (1) was unlikely, and the likely truth was a mutually reinforcing loop of (2) and (3) (that did eventually get broken in the United States with the Chinese Exclusion Act). I think the same dynamic is at play in South-South migration, with the difference that South-South migration today has at least some nominal level of border controls, and there’s enough of a global precedent of strict border controls that the learning curve towards very strict border enforcement can be (and in many cases, is being) traversed a lot faster.
Indeed, we can see this in India’s case today. There have been occasional bursts of effort to round up and deport illegal immigrants, often by governments that are prepared to basically “deport them all” — at least in principle. But if you’re used to US deportation numbers, you might laugh at passages like this:
Yet deportation under the Foreigners Act is also problematic. In 2003, the then Home Minister L. K. Advani ordered all states to deport illegal immigrants. A few weeks later 265 people were sent to the border, but authorities in Bangladesh declined to accept them. In fact India’s Border Security Forces (BSF), and its counterpart the Bangladesh Border Guards (then called the Bangladesh Rifles), came to the point of violence over the issue.
The deportation rates do seem to be increasing over time:
At the end of 2012, for instance, 16,530 Bangladeshi citizens with valid travel documents were found to be overstaying in India—while 6,537 and 5,234 Bangladeshi nationals were deported in 2012 and 2013, respectively.
And while the move towards newer, more effective forms of identification will probably mean that previous migrants get effectively amnestied, it may well make things harder for future migrants.
Overall, the level of preparedness and competence of the interior enforcement and deportation machinery at present seems to be comparable to what the US had for Chinese immigrants around the passage of the Chinese Exclusion Act. In both cases, natives are very unsympathetic, and many of them are openly virulent, to the immigrants. But the enforcement machinery is sporadic and erratic, and its throughput is minimal. Contrast this with “pro-immigrant” Barack Obama, who deported over 30,000 people a month, not so much because he personally hated immigrants, but because the deportation machinery was so well-established and functional that trying to slow it down it would be an expenditure of political capital — one that Obama didn’t consider necessary.
The terrorism problem
In the wake of the October 2014 Burdwan blast, close to the border with Bangladesh, carried out by an Islamic terrorist (or, in their view, revolutionary) group called the Indian Mujahideen, concerns about border security and terrorism were revived. The blasts revived concerns about Muslim madrassas (training institutes) as breeding grounds for terrorism Interestingly, Indian Muslim religious leaders (who do not necessarily represent the views of all or even most Indian Muslims, but are considered widely influential) sought to deflect this by stating that the problem wasn’t Indian Muslims, it was Muslims coming from across the border (i.e., Bangladesh). For instance, NDTV reports:
“No madrasa in India is anti-national. No Muslim in India is anti-national,” said Jamiat’s Sidiqullah Chowdhury. “The ones who come from outside are anti-nationals. Indian Muslims or madrasas are not terrorists.”
I believe that the threat of terrorism is in general greatly exaggerated because of its greater political salience and visibility, but it is still a threat that deserves to be taken somewhat seriously. Would an open border between India and Bangladesh lead to a dramatic increase in terrorist activity? I don’t know enough to offer a clear answer, though I’m hoping that posts later this year will explore the question more closely. But going by what we generally know about terrorism and its relation to migration policy, it seems that, to the extent that the threat of terrorism can be reasonably contained, it can be done through better targeted policy, and closing the border to economic migrants can in some ways complicate it. Consider, for instance, this discussion in the Daily Mail:
“The advantages they enjoy here are innumerable: immigrant-pockets which have proved to be excellent hideouts; a big metropolitan, Kolkata offers them concealment and its railway stations, namely Howrah and Sealdah, easy connectivity with the rest of the country,” the official added.
In other words, those with terrorist ambitions can conceal themselves among economic migrants, who are also undocumented and seek to evade detection. What would happen if the border were officially opened? Things could move in either direction: terrorists would be hiding within a larger population, so would be harder to detect. On the other hand, if peaceful migrants did not need to hide from the law, a documentation or identity scheme could be more effectively enforced, so that one could more reasonably presuppose that those who did not seek to get appropriate documentation had nefarious intentions. Also, the cooperation of the Bangladeshi government in combating terrorist activities could be enlisted more effectively if the Indian government weren’t getting in the way of peaceful migrants from Bangladesh. How do these competing considerations balance out? It’s hard to know a priori, and it’s possible that there will be an increase in terrorist activity, but I don’t think that it will be a significant increase.
This is similar to the point that my co-blogger John Lee made about the US-Mexico border, where he drew on statements by officials who actually work in law enforcement at border towns:
Simply put, if you want a secure US-Mexico border, one where law enforcement can focus on rooting out murderers and smugglers, you need open borders. You need a visa regime that lets those looking to feed their families and looking for a better life to enter legally, with a minimum of muss and fuss. When only those who cross the border unlawfully are those who have no good business being in the US, then you can have a secure border.
Co-blogger Joel Newman made some related points when discussing open borders, terrorism, and Islam:
So one argument notes that, unlike our current restrictionist policy which devotes considerable resources and focus on keeping out unauthorized immigrants seeking to work in the U.S., resources under an open borders policy could be focused on screening out terrorists. Another argument is that the free movement of people between countries could lead to the spreading of ideas contrary to those which inspire terrorism; immigrants who move between the U.S. or other western countries and their native countries would share values such as individual rights, tolerance, and democracy with their compatriots who remain in the native countries. A third argument is that if terrorism grows out of weak economies in native countries, the free movement of people from those countries and the resulting economic benefit to those countries (through remittances and immigrants returning to their native country to establish new businesses) could help prevent terrorism.
There is another reason open borders could help combat terrorism. Kevin Johnson, author of Opening the Floodgates, notes that “carefully crafted immigration enforcement is less likely to frighten immigrant communities—the very communities whose assistance is essential if the United States truly seeks to successfully fight terrorism.” (page 35) Without the fear of being the targets of immigration enforcement, immigrants would be more likely to cooperate with authorities in identifying individuals who are potential terrorists in the U.S. and assist with efforts against terrorist groups abroad.
Narendra Modi’s election rhetoric
Narendra Modi assumed office as the Prime Minister of India in May 2014. While campaigning for the election, Modi emphasized repeatedly that, once elected, he would aim to solve the problem of Bangladeshi illegal immigration. It wasn’t clear at the time whether his words, like most political manifestos, were mere promises, or whether he intended to follow through on them. Modi did make these pronouncements only when campaigning in Bengal and Assam, rather than using a national platform, suggesting that it might be more of a device to connect with and win over voters in the affected regions than a key component of his actual agenda.
Modi’s views on immigrants had some interesting twists. For instance, in February 2014, Modi made remarks to the effect that India’s borders would and should remain open for Hindus worldwide, but not for Bangladeshi Muslims. The “open for Hindus worldwide” idea would be similar to Israel’s Law of Return.
“As soon as we come to power at the Centre, detention camps housing Hindu migrants from Bangladesh will be done away with,” Mr Modi told a public rally at Ramnagar in Assam.
“We have a responsibility toward Hindus who are harassed and suffer in other countries. Where will they go? India is the only place for them. Our government cannot continue to harass them. We will have to accommodate them here,” he said.
Stating that this did not mean that Assam has to bear the entire burden, he said “it will be unfair on them and they will be settled across the country with facilities to begin a new life.”
Earlier, Hindus from Pakistan had arrived in Gujarat and Rajasthan, but Atal Behari Vajpayee during his prime ministership evolved schemes to accommodate them in different states, he said.
However, Modi has threatened deportation for the majority of Bangladeshi migrants, who identify as Muslim:
Narendra Modi has said that “Bangladeshis” will be deported if he comes to power, in his sharpest comments yet on illegal immigrants. They have been given the red carpet welcome by politicians just for votes, he said at a rally on Sunday.
“You can write it down. After May 16, these Bangladeshis better be prepared with their bags packed,” Modi said in Serampore in West Bengal, which shares a porous border with Bangladesh.
Modi accuses other political parties in West Bengal and Assam of encouraging such migration and helping the migrants obtain false documents so that they can vote — a variant of the electing a new people argument, a particularly extreme form of the general political externalities argument. I don’t know enough about the extent of actual voter fraud in West Bengal and Assam (although voter fraud in the US seems to be greatly exaggerated, the situation is likely to be quite different in India). I do think, though, that to the extent the problem is real, it is created to quite an extent by the illegal status that these people have. If one political party keeps announcing its agenda to deport you (even if it rarely executes on that agenda), and another political party, openly or tacitly, allows you to stay, who will you swear allegiance to?
Interestingly, even while disagreeing with specifics, most commentators have tacitly endorsed Modi’s overall frame of needing to restrict immigration from Bangladesh. For instance, the answers to a Quora question about Modi’s speech (YouTube video earlier in the post) defend a nation’s right to arbitrary selection of immigration policy, appealing to intuitive versions of the idea we here call citizenism and collective property rights. For instance, Syed Fuad, who identifies as Bangladeshi, writes:
I’m not an Indian, so it’s not for me to decide. But in my opinion, Narendra Modi shouldn’t take it easy. He, being the Indian Prime Minister, is accountable to Indian citizens. Addressing their issues should always come before anything else, even if it means taking strong and often unpopular stands on sensitive issues.
Narendra Modi’s proposed solution
For the first few months after being elected, Modi seemed to be quiet on the subject of Bangladeshi migration. I assumed that, like most campaign trail rhetoric, this too would not actually be executed.
However, around the end of November, Narendra Modi’s proposed solution was released. Quartz has a detailed review. Here are the highlights:
Prime minister Narendra Modi has indicated that his government is open to executing a land swap with Bangladesh that will iron out long-standing border disputes and help thousands of people who live along the 4,096.7 kilometer-long common land boundary.
The deal, once ratified by the Indian parliament (PDF) will redraw India’s boundary with Bangladesh, where New Delhi will cede 17160 acres of land, in return for 7110 acres and swap enclaves. Enclaves are areas which are surrounded from all sides by foreign territories. India currently has 111 enclaves belonging to Bangladesh, while Bangladesh has 51 such areas.
Modi, in a speech in Assam on Dec. 01, also assured that the land swap—which his own party had previously vehemently opposed—would stop illegal Bangladeshi migrants from entering into India.
“The government will utilise the India-Bangla land transfer agreement to seal all routes across the international border through which illegal Bangladeshi migrants have been entering Assam and creating havoc in the state,” the prime minister said.
Quartz notes many problems with Modi’s solution in terms of the stated aim of reducing the illegal immigrant population, but does not question the goals themselves.
What would I suggest?
For good or bad, Narendra Modi, thanks to his generally hardline reputation, has more leeway to make genuine progress with migration liberalization than most other prime ministers. Given his past record of rhetoric and action, he is relatively insulated from the charge of being soft on Bangladeshis or on Muslims. This gives him a Nixon goes to China opportunity.
Modi has made some surprise moves in that direction. I don’t know about the wisdom of the land swap per se, but insofar as it contradicts his own rhetoric and at least apparently concedes land to the other country, it shows how, as somebody with a hardliner image, he is able to take actions that people with a softer image might be afraid to take as it would make them look weak.
But the land swap does not solve the fundamental need for free movement: even after all these years, the villages of Bangladesh and West Bengal are intertwined. People have extended families across the border. People seek economic opportunity across the border (my co-blogger John Lee made a related point about the borders of South-East Asia and the Nusantara a while back).
Modi can take a bold step forward by proposing a free migration zone with Bangladesh of the same sort that India has with Nepal. If Bangladeshis can come and go as they please, they have few incentives to pretend to be Indian citizens or to vote for parties using fraudulent documentation. Most people from Nepal who come to India are secure in the knowledge that they are free to go back and forth, and feel little need to become Indian citizens because it makes very little material difference to them (of course, there will be some who want Indian citizenship after living in India for a long time, or if they want to travel to third countries). Bangladeshis could get to the same point.
Modi could combine the creation of legal channels for migration with user fees that are slightly greater, but not much greater, than the cost of migrating illegally and getting false documentation. He could also come up with creative ways of encouraging greater geographical spread of Bangladeshi migrants. He’s already given the matter some thought with regards to Bangladeshi Hindu refugees. I don’t know offhand what the ideal solutions would be, or even if the problems faced by the states adjacent to Bangladesh are serious enough to warrant action, but it might still be politically expedient for Modi to show he is doing something in that regard. For instance, there could be special trains for immigrants that, at a relatively low cost, transport the immigrants to specific states, and where the immigrants formally enter the country after getting off the train at the new state. (Incidentally, concerns that immigrants who land at a particular part of the country may just stay there rather than migrating to other parts of the country were also voiced by some officers at Ellis Island).
There is also the question of whether the Bangladeshi government will agree to a free migration agreement with India. If it doesn’t, the Indian government can still do something similar unilaterally, but perhaps with fewer bells and whistles, so as to encourage the Bangladeshi government to reciprocate. Overall, I believe that the case for free migration doesn’t depend on reciprocity, but it may still be politically expedient to negotiate the deal that way, to placate voters that India is getting something from the deal. Independently, there is probably some value in making it easier for Indians to move to and from Bangladesh. There are also trade and transportation advantages: reducing border tensions with Bangladesh can allow for easier transportation of goods and people between the North-Eastern states and the rest of India. Currently, due to the way the borders are structured, the North-Eastern states are connected to the rest of India via a very narrow region of land, making economic integration harder. The free migration agreement can accompany greater ease of movement of goods and people through Bangladesh between the North-Eastern states and the rest of India.
Why does this matter?
The place premium between Bangladesh and India is probably not large (it would approximately equal the GDP per capita ratio, which is less than 2). And the absolute gains per migrant aren’t large either. Why, then, is this important?
- The absolute population sizes in question are big enough. Allowing the 150 million Bangladeshis to move to India, seasonally or permanently, is a big deal even if the per capita gains aren’t huge. It creates a larger, more flexible, integrated labor market.
- There may also be a peace dividend: with less border tensions, the residents of the countries have more opportunity to collaborate, and the governments can better negotiate on other issues.
- The Indian government saves on some border and interior enforcement costs, though there may be some costs to setting up an efficient free movement system. But I suspect that those costs are less than the costs of setting up a border and enforcement process that actually works at the level that the US system does.
- The free movement zone can create a precedent for a larger free movement zone. Other countries like Sri Lanka and Burma could be encouraged to join at a later stage. And in the longer run, perhaps Pakistan could be part of the zone as well. Open borders between India and Pakistan are unlikely to happen in the near future, because of the usual problems facing open borders between hostile nations. I think a free migration zone offers the best bet.
- This is somewhat niche, but allowing free movement creates an insurance of sorts against adverse weather events, something that Bangladesh in particular is susceptible to because much of its land is low-lying and flood-prone. It is believed that climate change will exacerbate the problems that Bangladesh is facing. Free migration can possibly help avoid disaster striking suddenly. Similar points has been made by co-bloggers Joel and Nathan.
- From the open borders perspective, I believe that this is a critical time in the history of India’s immigration enforcement. This is a time when Indian record-keeping is finally getting good enough that the country can start building a systematic enforcement and deportation apparatus. If we start traveling down this road, it can be quite hard (though not impossible) to reverse or change course. I believe that the years immediately before and after the passage of the Chinese Exclusion Act had considerable importance in terms of the development of the basic immigration enforcement apparatus, as well as the legal precendents they created. India could be going through a similar phase. Putting a brake on the process could yield larger-than-meets-the-eye dividends in terms of an undesirable road not taken.
Related reading
Some of the links in this section are also present in the body of the article.
- Nepal and India: an open borders case study by Vipul Naik, Open Borders: The Case, March 21, 2014.
- South-South migration and the “natural state” by Vipul Naik, Open Borders: The Case, November 22, 2014.
- Open borders within India (part 1) by Vipul Naik, Open Borders: The Case, March 31, 2014.

 World Press 2014 photo: Signal from Djibouti, source
World Press 2014 photo: Signal from Djibouti, source 
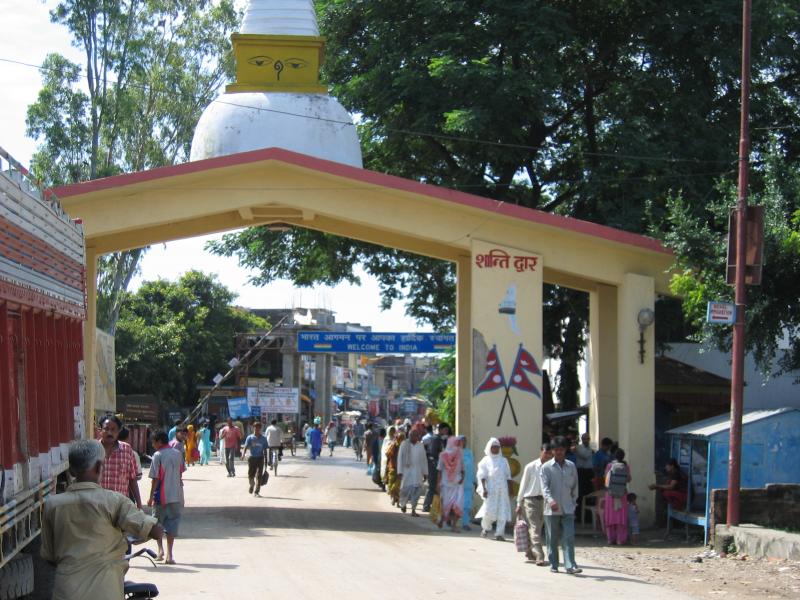 The open border between India and Nepal, source
The open border between India and Nepal, source